NEWS
News Center
News Center
NEWS

Shanghai Shang Shaft Bearing Quality Inspection Institute Co., Ltd.

Address: 301 Shangxue Road, Jiading District, Shanghai
Torque, torque, torque, what is the difference?
2022-03-02 15:02
Moment in physics refers to the tendency of an object to rotate around an axis or fulcrum. Moment, the physical quantity that the force produces a rotating effect on the object, can be divided into the moment of the force to the axis and the moment of the force to the point. The turning moment is also called torque or torque.
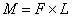
Moment in physics refers to the tendency of an object to rotate around an axis or fulcrum. Moment, the physical quantity that the force produces a rotating effect on the object, can be divided into the moment of the force to the axis and the moment of the force to the point. The turning moment is also called torque or torque.
The concept of torque can be seen everywhere in our daily life, from the seesaw we played when we were young to Archimedes' famous saying-"give me a fulcrum, I will pry the whole earth". These all reflect the meaning of torque. Similarly, torque is everywhere in cars, but through a series of rotation of the drive shaft, the torque here is called torque. The size of the torque directly affects the power output efficiency, energy consumption, and even operating life and safety performance and other factors.
Difference Between Torque and Moment
The range covered by the two is different, and the range of moments is broader. The result of multiplying all forces by the force arm can be called moments, but the torque generally refers to the moment received by the rotating object. For example, when the wheel rotates, the product of the ground friction force and the wheel radius is generally called torque, but it is also a type of torque. The use of a bottle opener to open a beer bottle is generally called torque, but not torque.
Difference Between Torque and Torque
The couple or moment that causes the machine element to rotate (including the tendency to rotate) is called the torque of rotation, or torque for short. Under the action of torque, any element must produce some degree of torsional deformation (which may include elastic deformation and plastic deformation). Therefore, it is customary to call the torque of rotation torque, or torque for short. The two can be mixed in any field, but torque is more commonly used in engineering.
Torque, torque and torque are the same in motors. Generally, in the same article or the same book, only one of the above three nouns is used, and it is rare to use two or more nouns at the same time. Although these three words are used differently, they all refer to the driving "moment" generated by the rotor winding in the motor that can be used to drive the mechanical load. The so-called "moment" refers to the force and the fulcrum and the force. The product of the distance perpendicular to the direction of action.
Previous Page:
: Next Page